

Hemodialysis centers, like other health care facilities, generate medical waste of a varying nature:
Each provider must implement a waste treatment procedure to handle the various types of waste generated. Therefore, it is important to segregate waste after care or a medical intervention has been performed.
In particular, implementing a waste segregation and disposal procedure for biohazardous waste is essential in preventing nosocomial infections (health care-associated infections).
The rate at which biohazardous waste is generated varies in hemodialysis centers and depends on the number of patients treated as well as the quality of segregation at the facility.
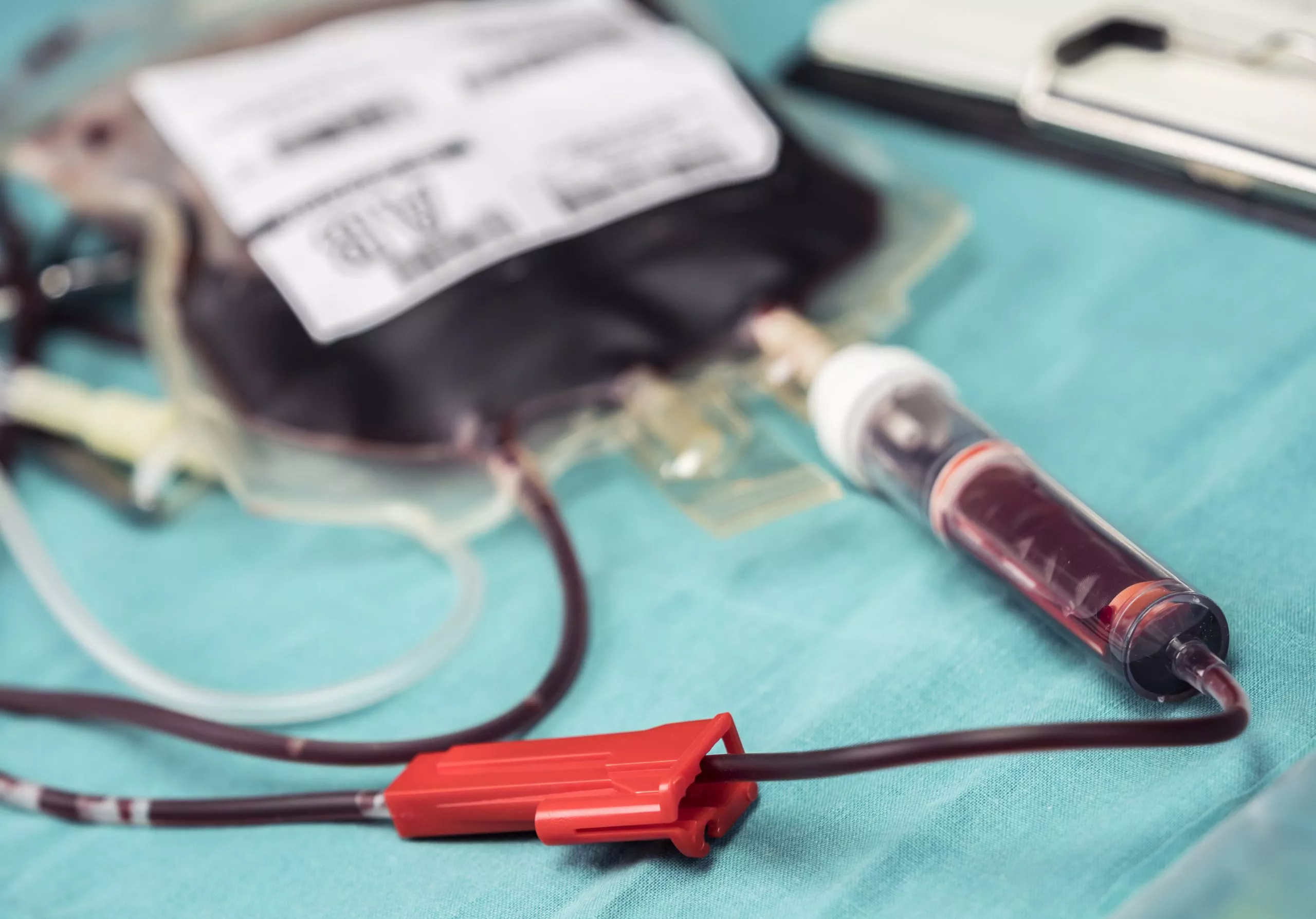
Biohazardous waste originating from hemodialysis centers comes essentially from the care provided to patients with kidney failure during treatment. Hemodialysis centers generate biohazardous waste of a varying nature:
In general, medical waste in hemodialysis environments is packaged in bags (that may be autoclaved or not), in biohazardous waste containers or drums.
Segregating and managing this waste satisfactorily is paramount. At these facilities, the quantity of biohazardous waste and the diversity in the number of people through its doors (patients, health care professionals, visitors) means that the biological risk must be controlled, not only for its people and the environment, but also to prevent cross-contamination and nosocomial infections.